Diabetes Mellitus Type II (DMII) is a chronic condition that affects millions worldwide, necessitating continuous monitoring and management. With advancements in technology, QR codes are emerging as an innovative tool to enhance diabetes management. This article explores the application of QR codes in the context of DMII (which are called DMII QR Codes), offering insights into how they can streamline patient care, improve access to critical information, and support healthcare providers in managing this complex condition.
Part 1. What is a Snapchat QR Code?
Understanding DMII:
DMII is a chronic condition characterized by insulin resistance, where the body's cells do not respond effectively to insulin, leading to elevated blood glucose levels. The management of DMII requires a holistic approach that includes lifestyle changes, regular monitoring, and medication. The complexity of these tasks can be daunting for patients, making it essential to explore new technologies that can simplify and improve the management process.
QR Codes in Medical Documentation and Information Sharing:
QR codes can be used to store and share critical medical information, such as blood glucose levels, medication schedules, and dietary plans. By scanning a QR code, patients or healthcare providers can quickly access up-to-date information, ensuring that all parties involved in the patient's care are on the same page. This is particularly useful in emergencies where quick access to accurate medical data is crucial.
For example, a patient with DMII could carry a QR code on their medical ID card or smartphone that links to their electronic health records (EHR). In case of an emergency, first responders or doctors could scan the code to immediately access the patient’s medical history, current medications, allergies, and other vital information. This reduces the risk of errors and ensures that the patient receives appropriate care promptly.
Part 2. QR Codes in DMII Management & How to Create
1. Medication Management
For individuals managing DMII, medication adherence is crucial. QR codes can be embedded on medication packaging or patient cards, linking directly to detailed information about the drug, including dosage instructions, potential side effects, and interactions. This ensures that patients have instant access to vital information, reducing the risk of errors and improving adherence to prescribed treatments.
How to Create a QR Code for Medication Management:
Step 1: Choose a QR Code Generator
Use a reliable QR code generator that allows you to create codes with embedded information or links to a website containing detailed data. Among the many QR code generation software on the market, iMyFone QRShow is one of the easier to use and more cost-effective.
- Generate QR codes for your links, documents, contacts, etc.
- Store and share medical information, such as blood glucose levels, medication schedules, and dietary plans.
- Customize your QR code with images, logos, frames, etc.
- Reduces the risk of errors and ensures patients receive appropriate care promptly.
Step 2: Input the Information
- If the information is short and simple, you can directly embed it into the QR code (text or vCard). For more complex or detailed information, create a dedicated webpage or PDF file with all the necessary details. Then, generate a QR code that links to this online resource.
- Take the text content as an example: Choose 'My QR code' > 'Create QR code'. Select 'Plain Text'. Then enter the vital information you need.
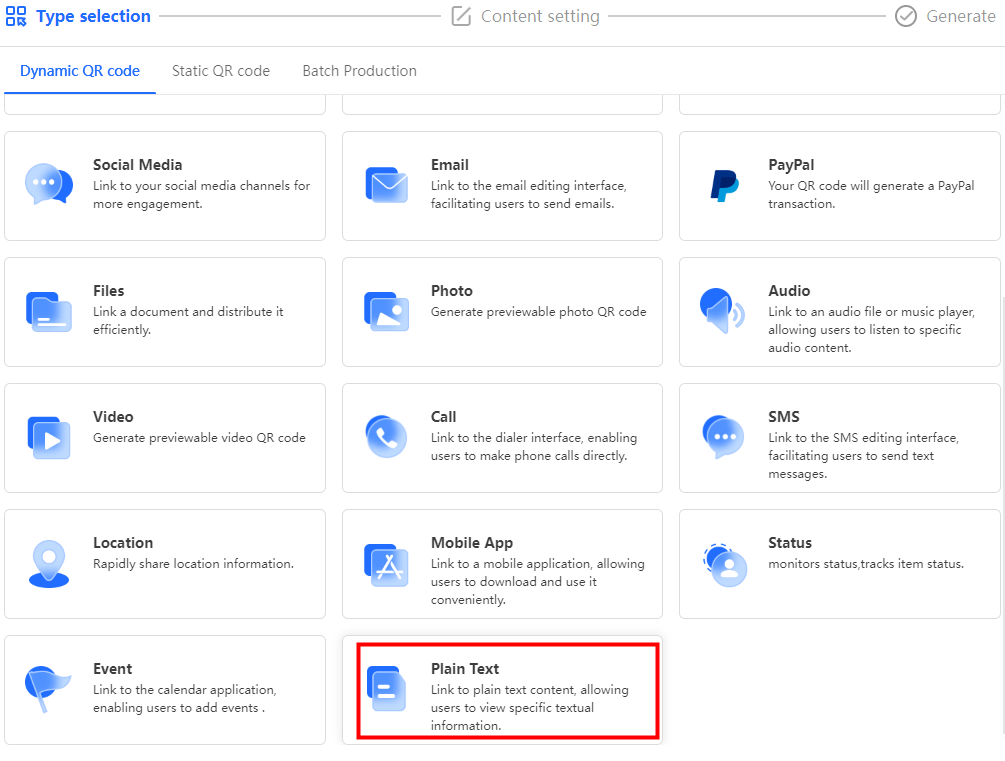
Step 3: Customize the QR Code (Optional)
- You can customize the QR code to include a logo, change its color, or modify its design to match the branding of the medication or healthcare provider.
- Eye-catching colors are more likely to attract patients' attention and focus.
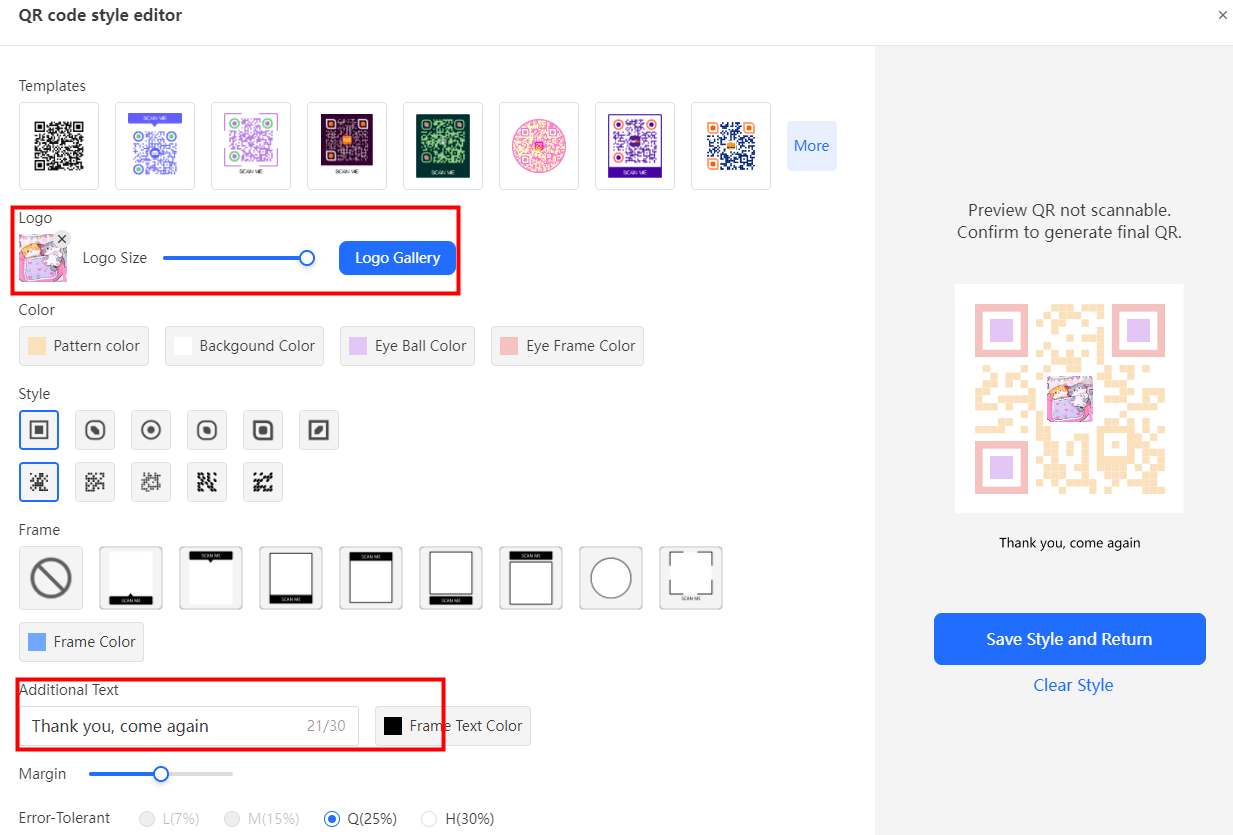
Step 4: Generate and Test the QR Code
- After designing your QR code form, click Generate and then choose the format you want to download.
- Before printing or distributing the QR code, test it on multiple devices to ensure it scans correctly and leads to the correct information. Check that all the links work, and that the information is clear and easily accessible.
2. Blood Glucose Monitoring
QR codes can simplify the process of tracking blood glucose levels. Patients can scan a QR code on their glucometer or testing strips, automatically logging their readings into a digital health record. This data can then be shared with healthcare providers in real-time, facilitating timely interventions and adjustments to treatment plans.
How to Create a QR Code for Blood Glucose Monitoring:
Step 1: Open iMyFone QRShow, and click “status” to add a new status.
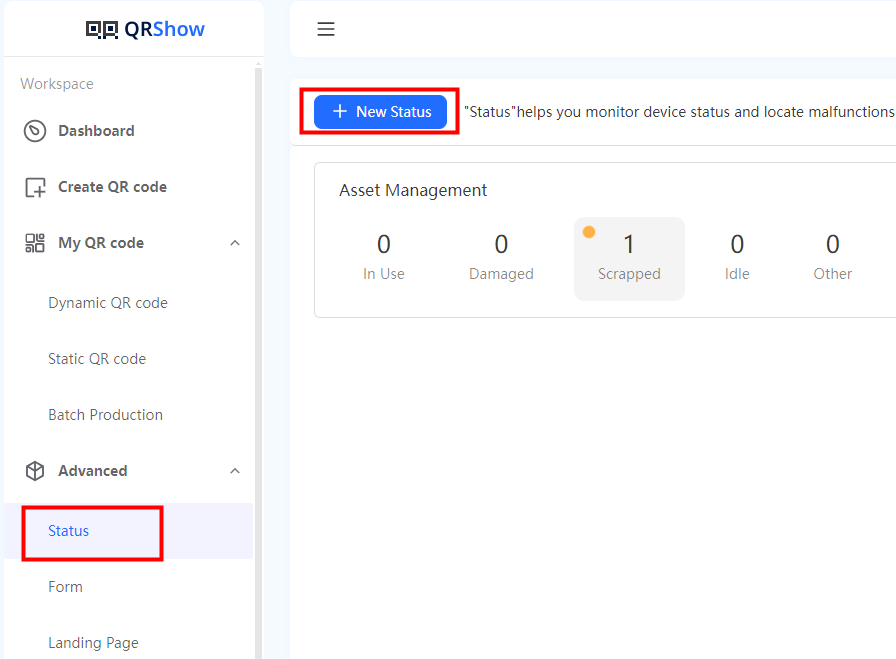
Step 2: Choose “New Status” for tracking the data you need, Take blood glucose monitoring data as an example.
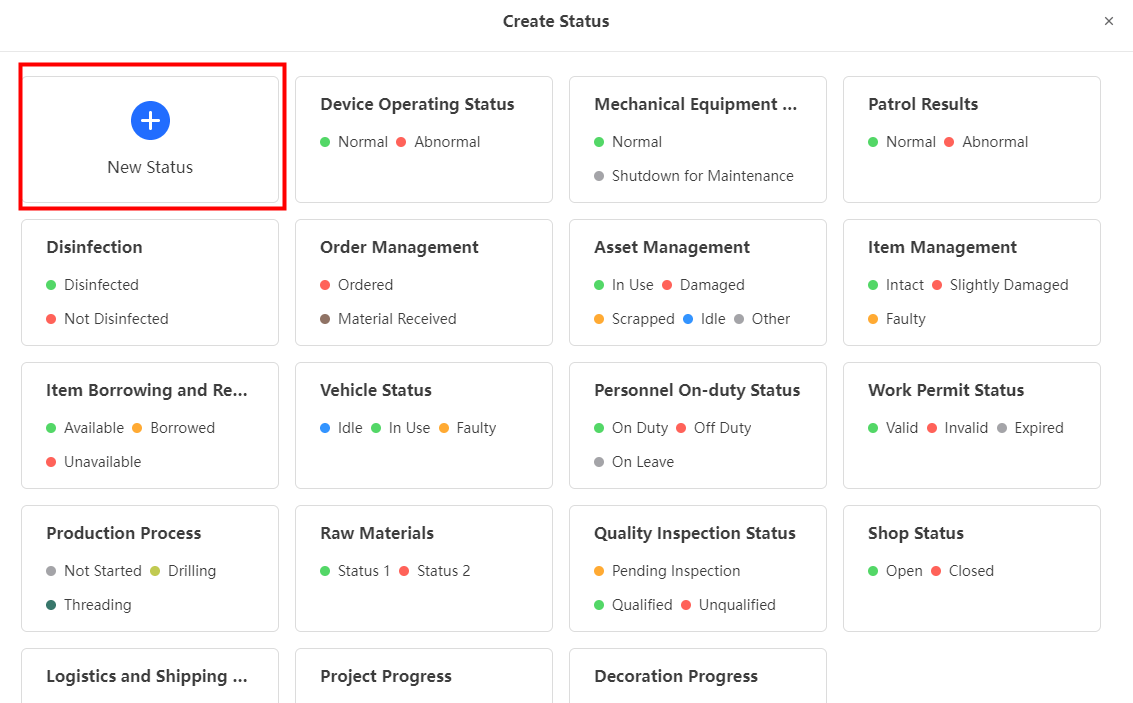
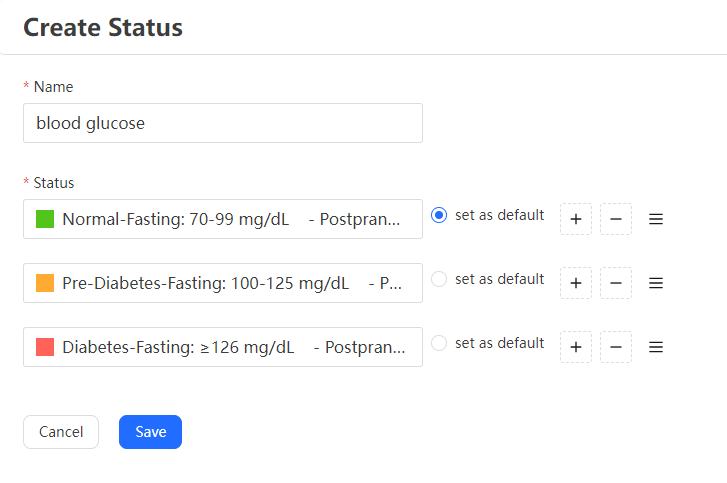
Step 3: Customize the QR Code (Optional).

Step 4: You can name this QR code before generating it to make it easier to search and view later.
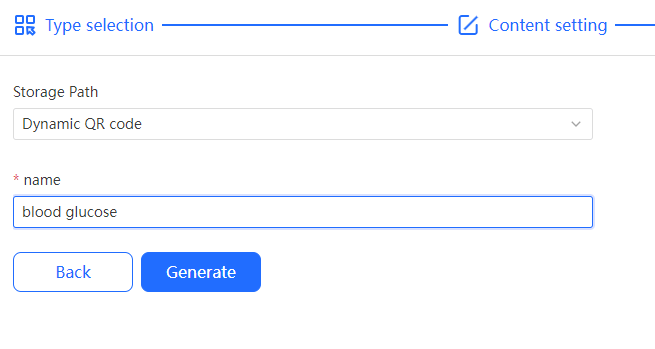
Step 5: Scan the QR code with your phone to record each blood glucose reading, and you can also mark specific data in the 'Mark' field. This way, you can monitor your blood glucose changes on the dashboard. Create now!
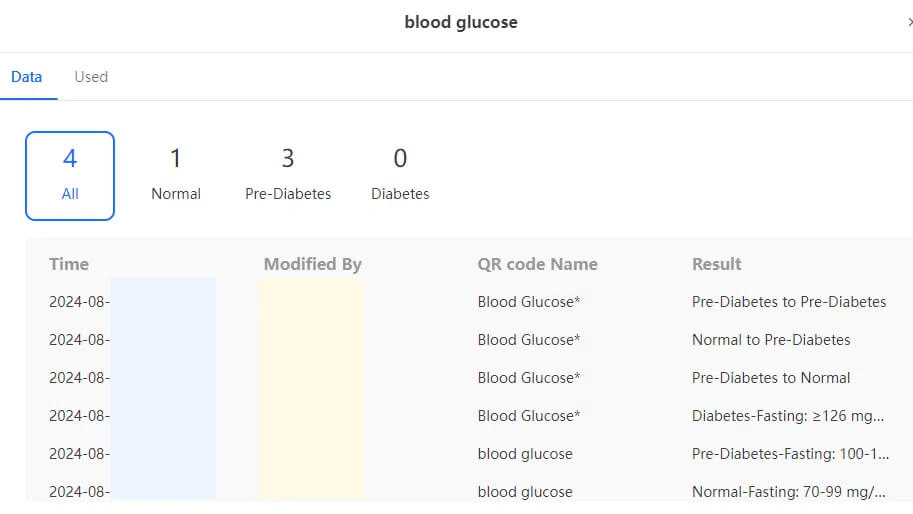
3. Dietary Guidance
Diet plays a significant role in managing DMII. QR codes can be included in meal plans, linking to nutritional information and recipes tailored to diabetic needs. By scanning the QR code, patients can access personalized dietary recommendations, helping them make informed choices and maintain stable blood glucose levels.
4. Emergency Response
In emergencies, quick access to a patient’s medical history is vital. QR codes can be printed on medical ID bracelets or cards carried by DMII patients. When scanned, the QR code can provide emergency responders with critical information such as the patient’s diabetes status, current medications, allergies, and emergency contacts, ensuring that appropriate care is administered swiftly.
Part 3. QR Codes for Healthcare Providers
1.Educational Resources and Patient Empowerment:
Education is a key factor in successful DMII management. QR codes can be linked to a wealth of educational resources, including videos, articles, and interactive tools that teach patients about their condition and how to manage it effectively. For instance, QR codes provided by healthcare professionals can link to tutorials on how to use a blood glucose meter, instructions for administering insulin, or tips for managing stress and its impact on diabetes.
These educational resources can be personalized to the patient's level of understanding, making complex medical information more accessible and easier to digest. By providing patients with the knowledge they need to manage their condition, QR codes can help empower them to take control of their health.
2.Facilitating Remote Consultations:
In the age of telemedicine, QR codes can play a vital role in facilitating remote consultations between patients and healthcare providers. Patients can scan a QR code to instantly connect with their doctor through a secure video call platform. This is especially beneficial for patients with mobility issues or those living in remote areas, where access to healthcare services may be limited.
Furthermore, QR codes can be used to share medical data before a remote consultation, ensuring that the healthcare provider has all the necessary information to make informed decisions during the appointment. This streamlines the consultation process and improves the quality of care provided.
Part 4. Tips for Using DMII QR Code
Determine the Information to Include
Medication Details: This could include the name of the medication, dosage instructions, potential side effects, interactions with other drugs, and expiration dates.
Patient Information: For patient cards, include the patient’s name, medical history, allergies, emergency contacts, and current medications.
Usage Instructions: Instructions on how to use the medication, including time of day, food interactions, and any other special considerations.
Contact Information: Include the contact details of the healthcare provider or pharmacy for easy access.
Educate Patients
Provide instructions on how to use the QR code. This might include explaining what a QR code is, how to scan it, and what type of information they can expect to access.
Consider offering demonstrations or providing a help guide, especially for older patients or those unfamiliar with QR code technology.
Update the Information as Needed
Regularly review and update the information linked to the QR code, especially if it changes (e.g., new medication instructions, changes in patient health status).
Ensure that any updates are reflected in the QR code data.
Part 5. Challenges and Future of QR Codes in Diabetes Management
While the potential of QR codes in DMII management is promising, there are challenges to consider. Ensuring patient privacy and data security is paramount, particularly when sensitive health information is involved. Additionally, there may be barriers to adoption among older adults or individuals with limited access to technology. Addressing these challenges requires thoughtful implementation and education to ensure that QR codes are accessible and beneficial to all patients.
The integration of QR codes into DMII management is still in its early stages, but the growth potential is vast. As technology continues to evolve, QR codes could become a standard tool in the management of chronic conditions like diabetes. Future developments may include more advanced applications, such as integration with wearable devices or AI-powered platforms that provide personalized treatment recommendations based on real-time data.
Conclusion
QR codes offer a versatile and innovative solution for enhancing DMII management. From improving medication adherence and dietary guidance to supporting remote monitoring and emergency response, iMyFone QRShow can play a crucial role in empowering patients and healthcare providers alike. As the healthcare landscape continues to embrace digital transformation, the adoption of QR codes in diabetes management is poised to become an integral part of comprehensive care strategies, ultimately leading to better outcomes for individuals living with Diabetes Mellitus Type II.







Rated Successfully!
You have already rated this article!